Nursing Care Plan for Mastoiditis
According to George (1997: 106), the clinical manifestations in patients with mastoiditis include:
- The fever usually disappear and arise.
- Pain tends to settle and throbbing, located around and inside the ears, and experience tenderness in the mastoid.
- Hearing loss.
- Tympanic membrane bulging contain skin that has been damaged and discuss sebaceous (fat).
- Posterior canal wall hanging.
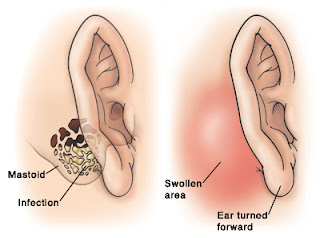
- Postauricular swelling.
- A large discharge through the ear canal and the odor.
Nursing Diagnosis and Interventions for Mastoiditis
1. Acute Pain is related to inflammation of the mastoid bone because of infection.
Goal: Pain is resolved.
Expected outcomes:
- Pain is reduced.
- Pain scale decreased.
- The face looked relaxed.
1. Review the scale of pain, location, intensity.
R /: Knowing the effectiveness of interventions.
2. Provide a comfortable position.
R /: Reduce pain.
3. Teach relaxation techniques and create a tranquil environment.
R /: Turning his attention to the pain and reduces pain.
4. Collaboration of analgesics, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory as indicated.
R /: It can reduce pain, kill germs and reduce inflammation and accelerating healing.
2. Hyperthermia related to the inflammatory process.
Goal: The body temperature may be normal (36 0- 37 0 C)
Expected outcomes:
- The body temperature within normal range (36 0-37 0 C).
- The skin does not feel warm.
- The face does not look red.
- Prevent dehydration.
Interventions :
1. Monitor the input and output.
R /: To find out the patient's fluid balance.
2. Measure the temperature every 4-8 hours.
R /: To determine the condition of the client's body temperature.
3. Teach warm compresses, and a lot of drinking
R /: To reduce body heat and replace lost body fluids.
4. Collaboration with the administration of antipyretics.
R /: To reduce the heat.