 |
| Empyema |
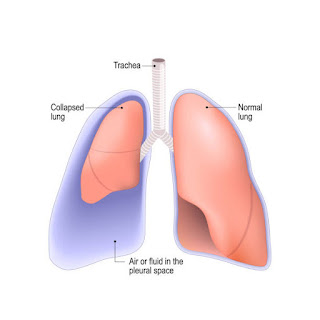
Empyema is defined as a collection of pus in the pleural cavity, gram-positive, or culture from the pleural fluid. Empyema is usually associated with pneumonia but may also develop after thoracic surgery or thoracic trauma. (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Empyema is usually caused by an infection that spreads from the lung. It leads to a buildup of pus in the pleural space.
There can be 2 cups (1/2 liter) or more of infected fluid. This fluid puts pressure on the lungs.
Risk factors include: Bacterial pneumonia, Tuberculosis, Chest surgery, Lung abscess, Trauma or injury to the chest.
In rare cases, empyema can occur after thoracentesis. This is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the chest wall to remove fluid in
the pleural space for medical diagnosis or treatment. (medlineplus.gov)
Symptoms of empyema may include: having a case of pneumonia that does not improve, a fever, chest pain, a cough, pus in mucus, difficulty breathing, a crackling sound from the chest, decreased breathing sounds, dullness when tapping chest, fluid in the lungs (visible with a chest X-ray).
Empyema can progress through three stages if a person does not receive treatment. (www.medicalnewstoday.com)
Nursing Diagnosis for Empyema
- Ineffective breathing pattern related to shortness of breath, mucus, bronchoconstriction, fatigue.
- Ineffective airway clearance related to increased secretions, ineffective coughing.
- Activity intolerance related to reduced oxygen supply.
- Self-care deficit related to fatigue.
- Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to anorexia.
- Impaired gas exchange related to ventilation-perfusion imbalance.
Related Posts :



